“【Leetcode】8-14"
[toc]
9.Palindrome Number
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. An integer is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
Example 1:
Input: 121
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: -121
Output: false
Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Example 3:
Input: 10
Output: false
Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
python solution:
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, x: int) -> bool:
if x < 0:
return False
else:
y = str(x)[::-1]
if str(x) == y:
return True
else:
return False
11.[Array]Container With Most Water
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, …, an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
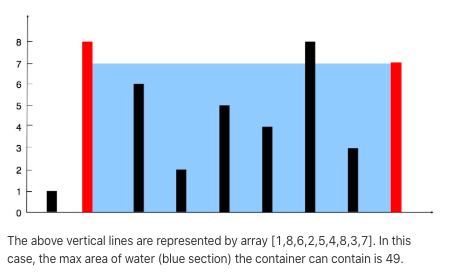
python solution 1(暴力解法:超时)
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
max_v = 0
volume = 0
for v in range(len(height)-1):
if height[v]<height[v+1]:
continue
else:
for j in range(v+1,len(height)):
volume = (j-v)*(height[j] if height[j]<height[v] else height[v])
if volume > max_v:
max_v = volume
return max_v
python solution 2(双指针)
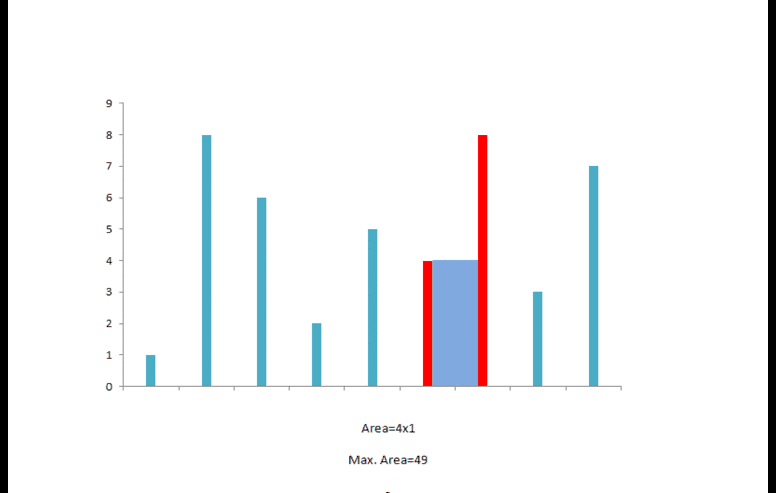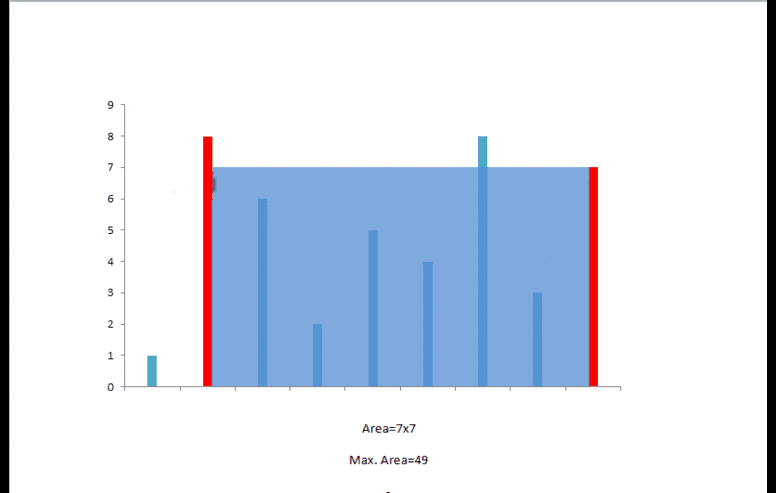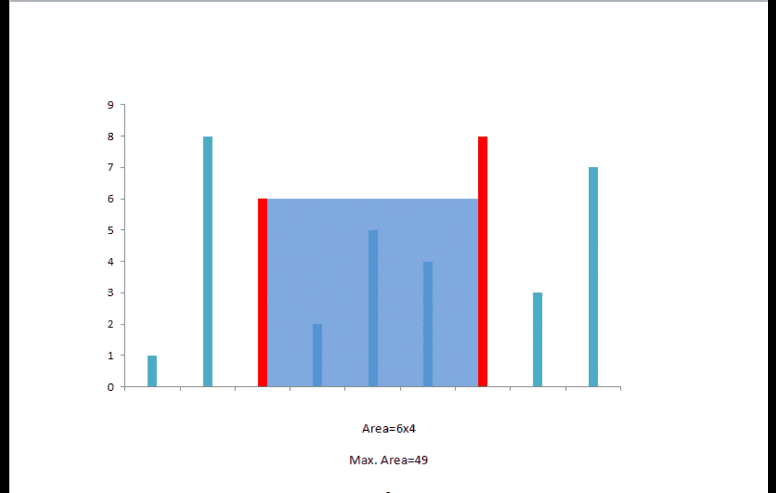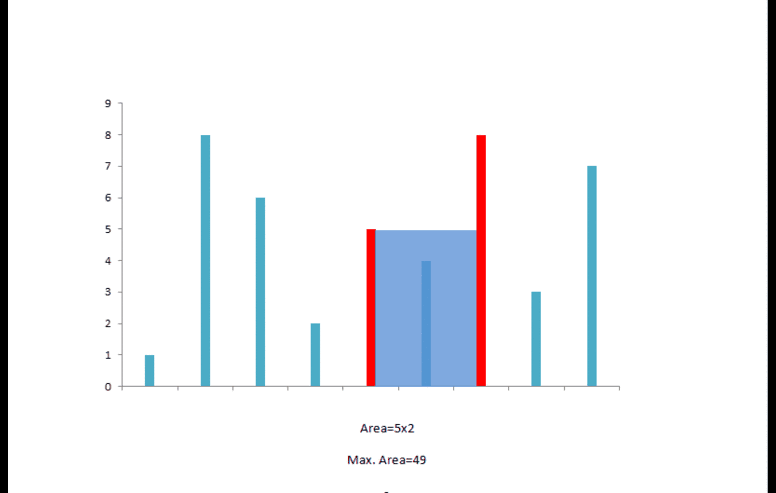
水的多少取决于底边长度,同时也与两边中较短边相关,两个指针同时从数组两端开始,同时记录下此时最大的体积.每次若长边向短边移动,对水量的多少没有帮助,而短边向长边移动则有可能获得更大的水量,如下所示.
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
max_v = 0
volume = 0
i = 0
j = len(height)-1
while i<j:
volume = min(height[i],height[j])*(j-i)
if volume > max_v:
max_v = volume
if height[i]<height[j]:
i += 1
else:
j -= 1
return max_v
13.Roman to Integer
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
For example, two is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one’s added together. Twelve is written as, XII, which is simply X + II. The number twenty seven is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900.
Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
Example 1:
Input: "III"
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: "IV"
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: "IX"
Output: 9
Example 4:
Input: "LVIII"
Output: 58
Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: "MCMXCIV"
Output: 1994
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
python solution: mine
class Solution:
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
d_1 = {'I': 1, 'V': 5, 'X': 10, 'L': 50, 'C': 100, 'D': 500, 'M': 1000,
'IV': 4, 'IX': 9, 'XL': 40, 'XC': 90, 'CD': 400, 'CM': 900}
d_2 = ['IV', 'IX', 'XL', 'XC', 'CD', 'CM']
num = 0
i = 0
while i < len(s):
if s[i:i + 2] in d_2:
num += d_1[s[i:i + 2]]
i += 2
else:
num += d_1[s[i]]
i +=1
return num
better one
class Solution:
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
d = {'I':1, 'IV':3, 'V':5, 'IX':8, 'X':10, 'XL':30, 'L':50, 'XC':80, 'C':100, 'CD':300, 'D':500, 'CM':800, 'M':1000}
return sum(d.get(s[max(i-1, 0):i+1], d[n]) for i, n in enumerate(s))
notes:
- 此处构建的罗马数字对照的字典:实际值-子串内左边罗马数字值
dict.get()方法:第一个值为要在字典里寻找的索引,第二个值为当第一个值没找到时的默认值enumerate方法,迭代器
14. Longest Common Prefix
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string “”.
Example 1:
Input: ["flower","flow","flight"]
Output: "fl"
Example 2:
Input: ["dog","racecar","car"]
Output: ""
Explanation: There is no common prefix among the input strings.
Note:
All given inputs are in lowercase letters a-z.
python solution:
class Solution:
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs):
"""
:type strs: List[str]
:rtype: str
"""
res = ""
for tmp in zip(*strs):
tmp_set = set(tmp)
if len(tmp_set) == 1:
res += tmp[0]
else:
break
return res
notes:
zip方法的作用类似于解压缩. 如果单zip(strs)会返回列表内所有元素,当在strs前加上*后,返回的组数是最短字符串的长度,每一组内的元素是每个字符串在相同位置的值set方法是清除重复元素